Lower Back Stretches for Men: How to Improve Mobility and Reduce Pain After 40
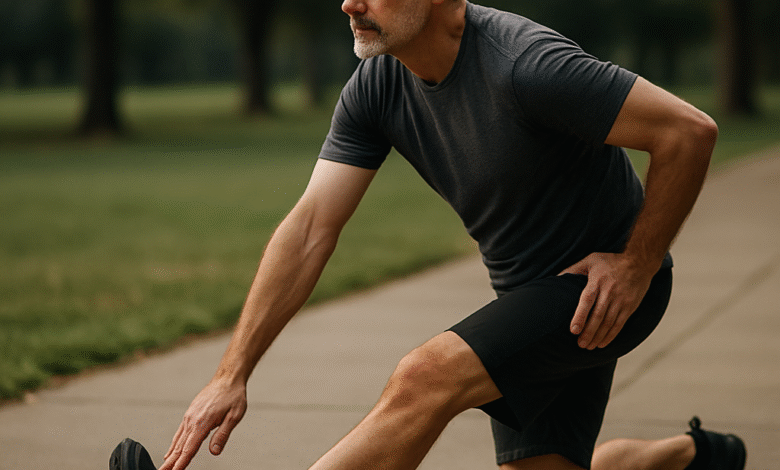

Ever get that nagging tightness in your lower back after sitting through a long meeting or even just getting out of bed? You’re not alone. For men over 40, lower back stiffness can sneak in and steal your day if you don’t catch it early.
It’s a familiar scenario: you wake up, grab your coffee, and think, “Why does my back feel like it’s been through a wrestling match overnight?” Here’s the thing—our bodies just don’t bounce back the way they used to after 40. That’s not some doom-and-gloom; it’s biology meeting lifestyle. Years of desk jobs, weekend warrior habits, or just plain ignoring those subtle aches add up.
So, why care about lower back stretches for men? Because they’re your frontline defense. Stretching isn’t just a warm-up or cool-down fancy move for athletes. It’s the daily oil that keeps your spine flexible, muscles loose, and joints happy. Without it, you risk that tight, painful lower back becoming a chronic issue, messing with your workouts, your mood, even your sleep.
And if you’re thinking, “I’m too busy to be doing stretches,” I get it. But here’s the kicker — even a few minutes of targeted stretching can change your whole day. Imagine standing straighter, moving easier, and finally shaking off that stiffness that sticks around like unwanted company.
This isn’t about becoming a yoga master or spending hours on the mat. It’s simple, practical moves designed for your midlife body. Whether you’re already active or just starting to pay attention to your health, knowing the right stretches is a game-changer.
Ready to feel a little better, a little looser, without any fancy equipment or awkward poses? We’ll break down easy, effective lower back stretches for men that fit into your busy schedule — no fluff, just what works. Let’s dive in.
If you want to complement these stretches with safe strength building to support your back and overall fitness, check out our guide on strength training for men over 40.
TL;DR: Quick Overview of Lower Back Stretches for Men
Lower back stretches for men aren’t about bending like a pretzel or mastering fancy moves. It’s about simple, targeted stretches that loosen tight muscles, ease stiffness, and keep you moving freely.
Think gentle twists, knee-to-chest pulls, and hamstring stretches—done regularly, even five minutes can make a difference. This isn’t just for athletes; it’s your daily reset to stop that nagging ache from settling in.
Step 1: Preparing Your Body for Lower Back Stretching
Look, before you dive headfirst into any lower back stretches for men, there’s a critical step many of us skip: prepping the body. If you’ve ever tried to stretch cold muscles, you know it doesn’t end well—tight, stubborn muscles just snap back, and that nagging ache could get worse. So, warming up isn’t a ‘nice-to-have’; it’s your best friend.
Think about what your lower back really needs. It’s not just about the muscles right there; it’s about everything connected—your hamstrings, hips, and even calves. When these areas get tight, your lower back takes the hit. So, before we stretch, we need to loosen those buddies up.
Why Hamstrings Matter More Than You Think
Ever noticed how your lower back stiffens after sitting all day? That tightness isn’t always your back crying for help — sometimes it’s your hamstrings acting up. Those muscles at the back of your thighs control a lot of the hip movement, and if they’re tight, your back overcompensates.
Milo Bryantis, a performance coach in his 50s, points out that after 40, keeping your hamstrings flexible isn’t just for athletes—it’s essential for everyday movement. Walking hamstring stretches and gentle leg swings get these muscles firing properly, reducing strain on your lower back.
Easy Moves to Kickstart Your Body
Here’s a simple warmup you can try right now, no fancy equipment needed:
- Walking Hamstring Stretch: Stand tall, take a small step forward with your right foot, and extend that knee slightly. Push your hips back and lean forward, feeling the stretch in your right hamstring and calf. Hold briefly then take three light steps to loosen up before switching legs.
- Walking Leg Kicks: With your chest up and core tight, step forward with your right foot and kick your left leg up straight ahead as high as comfortable. Alternate legs, keeping your back flat and avoiding any arching. This does double duty loosening hamstrings and activating your hip flexors.
These moves wake up your legs and lower back without forcing anything. They prep your muscles to move instead of cramp up—and that means your stretches will hit where they’re supposed to, not just push tension around.
Don’t Forget the Core and Posture
One more thing before any stretch: engage that core. I know, everyone says it, but it’s critical, especially for men in midlife managing lower back troubles. A strong core supports your spine and helps maintain good posture during stretches, reducing the risk of injury.
Stand tall, pull your navel toward your spine, and imagine a string gently pulling the top of your head upward. That’s your starting point. Keep that feeling through your warming up and stretching sequences.
So, what’s next? After these warmups, your body will be primed for effective lower back stretches that actually relieve pain and improve mobility. Skipping this step? You’re just setting yourself up for frustration or worse. Consistency here is where the real gains live.
Want the full recipe for building strength safely in midlife? Check out our detailed guide on strength training for men over 40, which includes tips on recovery that tie directly into improving flexibility and back health.
Remember, the body isn’t just parts; it’s a system that needs attention all around, especially after 40. Prep smart, and you’ll stretch smarter.

For more on how these movements help, the experts at Men’s Health explain the importance of hamstring flexibility for lower back health. And when you want a deeper look at how strength and flexibility work together as we age, the National Institute on Aging offers insights that make it clear: a little prep work goes a long way.
Step 2: Essential Lower Back Stretches for Men Over 40
If you’ve hit your forties, you might have noticed your lower back isn’t quite as forgiving as it used to be. The aches, the stiffness—that familiar nagging feeling after sitting too long or waking up stiff. Sound familiar?
Here’s the real talk: aging tends to stiffen muscles and joints, especially in the lower back. But it doesn’t have to be a one-way ticket to discomfort. Carefully chosen stretches can be a game changer, helping to loosen tight spots, improve mobility, and even reduce pain. So, let’s get into the essential lower back stretches for men over 40, with practical steps that make sense in real life.
Why Lower Back Stretches Matter After 40
Your spine is like the central pillar of a building. Over the years, that pillar can get a bit slanted if the muscles around it weaken or tighten. Doing lower back stretches regularly increases flexibility, helps relieve muscle tension, and improves your range of motion. Not to mention, it stimulates blood flow to the area, which supports nourishment and healing.
And here’s what most guys over 40 don’t realize: without working on flexibility, you’re basically setting yourself up for more aches and even injury. Stretching isn’t some soft option—it’s functional, preventative ‘maintenance’ for your back.
Top Lower Back Stretches You Can Start Today
Let’s break down a few key moves that are safe, effective, and don’t require any fancy equipment. You can do them at home or even during a work break.
1. Double Knee-to-Chest Stretch
Lie on your back and slowly pull both knees toward your chest. Hold for around 20-30 seconds while focusing on breathing easy. This stretches your lower back and glutes, soothing tension.
Tip: If pulling both knees feels tough, try one knee at a time. No rush—go at your own pace.
2. Cat-Camel Movement
On all fours, arch your back slowly toward the ceiling (cat pose), then gently drop it down toward the floor (camel pose). Repeat 10 times, moving with your breath. This helps improve spinal mobility and releases tight connective tissue.
3. Child’s Pose
From your knees, sit back onto your heels and stretch your arms forward on the floor, lowering your chest. Hold for 20-30 seconds. This gentle position stretches the lumbar area and calms the nervous system.
4. Supine Twist
Lie flat on your back and bend your knees. Let them slowly fall to one side while keeping your shoulders flat. Hold for 20 seconds and switch sides. This rotation helps relieve stiffness and balances muscular tension across the spine.
Precautions You Should Keep in Mind
Stretching feels great, but if something causes sharp pain or pins-and-needles sensations, stop immediately. And if pain radiates down your leg, or you notice numbness or weakness, that’s a red flag—check in with your doctor before pushing further.
Also, consistency beats intensity here. Five to ten minutes daily beats an hour on Sunday, every week. Give your body space to adapt, and those stretches will pay off over time.
Bonus: Combine Stretches with Breathing
Try engaging in slow, deep diaphragmatic breathing during these stretches. It’s not just about relaxing—it’s about helping your muscles release tension. When you breathe deep, your belly expands, oxygen flows better, and pain signals slow down. Take a moment to feel how this helps—the simplest things are often the best.
If you want a quick visual guide to these moves, here’s a helpful video that walks you through the essentials with proper form and timing:
Why not make walking and stretching your new best friends?
Walking regularly boosts blood flow and overall back health, and pairing it with these essential stretches creates a winning combo. According to experts at AARP, movement is key to managing lower back pain without over-reliance on meds or invasive treatments.
Also, research from the National Institutes of Health highlights that combining flexibility, aerobic exercise, and core strength is the best way to reduce chronic low back pain, especially as we get older. It’s not about busting out heavy workouts—but smart, steady care.
And don’t overlook how core stability underpins back health. Supporting muscles around your spine matter just as much as the stretches themselves. Strengthening these with gentle stabilization exercises complements everything you’re doing here.
So, grab a mat or just a comfortable space, and start with these stretches. Do them a little every day, and your lower back will thank you. Before you know it, you’ll move better, feel stronger, and maybe even forget when that stiffness crept in.
Step 3: Combining Lower Back Stretches with Core Strengthening
Alright, let’s talk about the secret sauce that really makes a difference for lower back health after 40: pairing those lower back stretches with solid core strengthening.
You might be wondering, “Why bother with core workouts if I’m already stretching my back?” The thing is, the core isn’t just about those six-pack abs you see in magazines. It’s a whole system of muscles around your torso that keep your spine stable and supported.
Think of your core like the foundation of a house. If the foundation is weak or cracked, it doesn’t matter how sturdy the walls are — things start to give way. Your core muscles, from the deep transverse abdominis wrapped like a corset around your abdomen, to your lower back muscles, and even the glutes, all play a part in holding you up and protecting your spine from strain.
Here’s the thing I’ve seen with guys over 40 trying to fix their lower back issues: they stretch but skip the strength work. The back stays bendy but the support isn’t there to keep it safe. And that’s a recipe for recurring pain or injury.
Core Strengthening Exercises That Pair Well with Lower Back Stretches
You don’t need to spend an hour in the gym. Fifteen or twenty minutes mixed between some lower back stretches is enough to start making a real difference.
Try these three beginner-friendly moves first:
- Bridge: Lie flat on your back with knees bent, feet hip-width apart. Squeeze your glutes and lift your hips off the floor until your body forms a straight line from shoulders to knees. Hold for a few seconds, then lower slowly. It’s like turning on a natural brace that supports your lower spine.
- Modified Plank: Starting on your hands and knees, lower onto your forearms. Keep your back straight like a plank of wood—not sagging or arching. Tighten your belly and hold for 10–20 seconds. This targets your whole core without stressing your lower back.
- Opposite Arm and Leg Raise: On all fours, extend your right arm forward and left leg back at the same time, keeping your hips square. Hold briefly and switch sides. The slow, controlled movement strengthens your core stabilizers and balance at once.
These moves specifically engage multiple core muscle groups, acting as a dynamic corset for your back. Harvard experts highlight that moves like bridges and planks build rigidity from your rib cage to your pelvis, creating the stable base your back needs to move without pain (Harvard Health).
But what about crunches or sit-ups? Honestly, those old-school moves often do more harm than good, especially after 40. They can stress your neck and overwork hip flexors, which pulls on your lower back — not what you want when you’re trying to heal or protect it.
Why Combining Stretches with Core Work Helps
Stretching keeps your muscles loose and flexible; strengthening keeps them stable and ready to support you in day-to-day tasks. This combo reduces pain and improves function, according to a detailed analysis of studies comparing core stability exercises to general workouts for low back pain (National Center for Biotechnology Information).
The research showed that people doing targeted core exercises saw better pain reduction and function improvements in the short term than those doing general exercises alone.
That’s because the core acts like a control center. When it’s strong and firing right, your lower back isn’t left to carry the whole load. You get better posture, improved balance, and less risk of irritating those sensitive spinal muscles and disks.
So, what should you do next?
Start slow and be consistent: Pick 2-3 core moves and 2-3 lower back stretches. Do them daily or at least every other day. Quality beats quantity here. Focus on control and smooth breathing, not rushing through reps.
And set a reminder. If you wait till you “feel like it,” it won’t happen. Carve out that five or ten minutes before or after your stretching routine—it’s your back’s best shot at feeling stronger.
| Exercise | Focus Area | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bridge | Glutes, Lower Back, Core Stabilizers | Builds rigidity from pelvis to rib cage; protects lumbar spine |
| Modified Plank | Abdominals, Shoulders, Core | Improves overall core strength; supports posture and reduces spinal load |
| Opposite Arm and Leg Raise | Core, Balance, Glutes, Shoulders | Enhances core coordination and spinal stability; improves balance |
| Lower Back Stretches | Back Muscles, Spine | Increases flexibility; decreases stiffness and back pain risk |
Remember, combining these lower back stretches for men with core strengthening is a game changer. It’s not about pushing hard but about smart, steady tuning up of your body’s natural support system.
Stick with it, and soon you’ll notice how your back moves easier—and how that nagging stiffness might finally start to fade.
Step 4: Creating a Daily Lower Back Stretch Routine That Works
Look, if your lower back feels like it’s carrying more than it should—like that stubborn middle-aged baggage we all pick up—you’re not alone. The good news is, setting up a daily routine with the right stretches can make this a thing of the past.
But how do you turn a vague “I’ll stretch more” wish into an actual, sustainable habit? Here’s the trick: keep it simple, consistent, and genuinely doable.
Start where you are, not where you want to be
Think about those mornings when you wake stiff and begrudgingly roll out of bed. Those moments are the perfect time to slip in some stretches. You don’t need fancy equipment or an hour. Even five to ten minutes can set your back up for success.
Begin with a couple of stretches that feel approachable. Lying on your back, try drawing one knee up to your chest. You’ll feel that gentle pull across your lower back—it’s like telling those muscles, “Hey, loosen up.” Hold for about 20–30 seconds, then switch sides. Simple.
Or roll your knees side-to-side while keeping your shoulders flat—this gets your spine moving and wakes things up without any pressure. If you want to sneak in more, the Mayo Clinic recommends repeating these stretches a few times, morning and evening, to build flexibility without strain.
Build your routine like stacking blocks
Once you’re comfortable, layer on a few more stretches focused on your lower back. Here’s a quick rundown of some moves that won’t take much brain space but pack a punch:
- Cat-Cow stretch on hands and knees—to get your spine flowing like a gentle wave.
- Child’s pose—offers a great passive stretch and relaxation.
- Seated forward bend—good for the back and hamstrings, which can really tighten as we age.
These moves don’t just stretch the lower back; they work surrounding muscles too, which, honestly, is key to keeping pain at bay.
Wondering if you should push further? It’s tempting but hold back from forcing deeper stretches, especially if something feels off. The goal is relief, not regret.
Make it stick: Routine wins over intensity
Here’s something I’ve learned the hard way over the years: you’re much better off doing a gentle routine every day than exhausting yourself once in a blue moon. Plenty of men over 40 report that consistency, even just ten minutes, wins the day for easing stiffness and guarding against aches.
Set an alarm. Tie your stretching to something you already do—maybe right after brushing your teeth or first thing before the coffee kicks in. If you let it slide till motivation appears, you’re in for a long wait.
Feeling impatient? Remember, Bupa points out that flexibility builds slowly. It’s not a race, and your back will thank you for the steady love.
Don’t ignore signals
Listen to your body. If a stretch creates sharp or shooting pain, stop immediately. If there’s an old injury or persistent discomfort, talk to your doctor or a physical therapist. They can help tailor a routine that suits exactly where you’re at.
Ready to get started today? Choose 3–4 stretches you like from above, keep your sessions short, and build that daily habit. Your lower back isn’t just a part of your body—it’s part of your second act. Treat it well, and it’ll carry you through plenty more adventures.

Step 5: When to Seek Medical Advice and Modify Your Stretching
Okay, so you’ve been building a daily habit of those lower back stretches for men, and maybe you’re feeling better—or at least not worse. But what if something feels off? That nagging twinge that won’t quit, or maybe sharp pains sneaking in when you least expect it? It’s easy to brush those off, especially when you’re busy juggling work, family, and life after 40. But here’s the thing: your back’s sending you messages, and sometimes, it’s shouting.
Know when to pause and listen
If a stretch ever causes sharp, shooting pain or a burning sensation, stop immediately. That’s your body waving a red flag. It’s not just about discomfort—it’s about preventing injury. Mild soreness after a stretch? Totally normal. But stabbing pain or numbness means it’s time to hit pause and reassess.
People with old injuries, chronic back issues, or persistent discomfort should definitely check in with a healthcare professional before pushing further. A doctor or physical therapist can pinpoint exactly what’s going on and help customize your routine to your unique needs. You don’t have to figure it all out alone.
When medical advice becomes crucial
Now, you might wonder, “When is it actually necessary to see a doctor?” Think about any persistent pain lasting more than a few weeks, especially if it’s waking you up at night or comes with weakness, numbness, or tingling down your legs. These signs could hint at something more serious, like a nerve issue or underlying condition that needs professional care.
Also, if your lower back pain started after a fall, accident, or sudden injury, don’t wait. Getting a thorough checkup ensures you’re not missing anything needing immediate treatment.
Modify your stretching routine wisely
Once you’ve got the green light from your healthcare provider, you might need to tweak your stretching routine. That could mean avoiding certain positions or focusing on gentle, targeted movements that protect your back while improving flexibility.
Sometimes adding complementary treatments—like chiropractic adjustments, which some men find helpful—can work alongside your stretches to ease stiffness. Just make sure to consult licensed professionals for safe care, like the recommendations from Cleveland Clinic on chiropractic adjustments.
Don’t ignore unusual symptoms
It’s also critical to be vigilant about unusual or persistent symptoms beyond just pain. For example, unexplained weight loss, constant fatigue, or changes in bladder or bowel habits could signal serious health issues, including some cancers. It’s uncomfortable to think about, but catching these early can make all the difference. Experts at MD Anderson Cancer Center highlight that persistent back pain sometimes masks bigger problems, so don’t hesitate to see your doctor if something feels wrong.
Finally, if any stretch or movement leaves you feeling strangely weak, dizzy, or causes numbness, reach out to a healthcare provider right away. These aren’t normal side effects and need prompt attention.
So, what should you keep in mind going forward? Stretch smart, stay tuned to what your body says, and don’t be afraid to ask for help. Lower back stretches for men over 40 are an amazing tool—but only when they play nicely with your body’s reality.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Lower Back Health Starting Today
Look, if you’ve made it this far, you’re already ahead of the game. Lower back pain is no joke—not just a minor annoyance but something that can sneak up and steal your energy, your focus, even your joy. And honestly, it feels like the body starts betraying you once you hit 40, doesn’t it? But here’s the thing: you’re not stuck with that fate.
Doing lower back stretches for men isn’t about becoming some yoga master or spending hours on the mat. It’s about those few minutes you carve out for yourself, respecting your body’s signals, and staying consistent. Think about it as an investment in all the things you love—keeping up with your kids, staying sharp at work, or finally hitting the golf course without wincing on the first hole.
So what should you do next? Start small. Pick a couple of stretches from what you’ve learned. Make it part of your morning or wind-down routine. And pay attention—if something feels off, don’t shrug it away. Reach out to a pro. The goal here isn’t just to ease pain; it’s to regain control over your body so you can keep climbing that second summit with confidence.
Remember, this isn’t about fighting age—it’s about living well after 40. You’ve got this.
FAQ: Common Questions About Lower Back Stretches for Men Over 40
Look, it’s totally normal to have questions when you’re starting to add lower back stretches into your routine—especially after 40 when your body isn’t as forgiving as it used to be. Let’s tackle some of the most common ones so you don’t have to guess or worry.
Q1: How soon can I expect relief from lower back pain after starting these stretches?
Honestly, this varies a lot depending on how long you’ve been dealing with the discomfort. Some men feel better within a week or two of consistent, gentle stretching. Others might need a month or more. The key is consistency and listening to your body. If you stretch daily—even 5 to 10 minutes—you’re helping your muscles loosen up and your joints regain mobility. Just don’t push through sharp pain; that’s a red flag.
Q2: Can lower back stretches actually prevent future pain episodes?
It’s a big yes, but with a catch. Stretches are a powerful tool to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tightness that often triggers back pain. Combined with good posture and strengthening exercises, they can lower your risk of flare-ups. But remember, back pain sometimes sneaks in due to sudden moves or lifting something heavy the wrong way. So, think about stretches as part of a bigger game plan—kind of like oiling the hinges before a door starts squeaking.
Q3: Should I be worried about hurting myself while stretching?
It’s smart to be cautious, especially if you’re over 40 and maybe haven’t been super active. Start slow, ease into each stretch, and avoid bouncing or forcing your range of motion. If something doesn’t feel right or triggers sharp or shooting pain, stop immediately. And if you have a history of serious back issues, chatting with your doctor or a physical therapist before starting is a safe bet.
Q4: Do I need any special equipment or a gym membership for these stretches?
Not at all. Most lower back stretches for men can be done at home with just a yoga mat or even on a carpet. Some guys find a foam roller or resistance bands helpful later on, but you don’t need them to get started. The beauty of this is that it’s simple and affordable—perfect for busy midlifers balancing a million things.
Q5: How often should I really stretch my lower back?
Try for daily or at least 4-5 times a week. It doesn’t have to be a big time commitment—10 minutes will do the trick. Consistency helps keep your muscles loose and prevents that nasty stiffness that comes with sitting too long or skipping movement days. Think of it as brushing your teeth: routine maintenance that keeps small problems from becoming big ones.
Q6: What if I don’t notice any improvement? Does this mean stretching won’t help me?
Not necessarily. Back pain has many causes, and sometimes stretching alone isn’t the whole answer. If after a few weeks you’re not seeing progress or your pain worsens, it’s wise to see a healthcare professional. According to the Mayo Clinic, most back pain improves with home care, but persistent or severe pain needs expert advice.
Q7: Is there an age limit for starting lower back stretches?
Absolutely not. Men over 40, 50, or even 60 will benefit from improving their flexibility and mobility. In fact, as NHS guidelines suggest, staying active with regular stretching is crucial to combat the natural aging process and maintain independence. You just might want to modify intensity and pace based on where you’re starting from.
So, what should you do next? Pick a stretch or two from your routine and commit to doing them regularly. Pay attention to how your body reacts—don’t ignore discomfort, but don’t be afraid to gently push past stiffness. Over time, these simple moves can change the game for your lower back and your whole day.